Spring
Springs are fundamental mechanical
components which form the basis of many mechanical systems. A spring can be
defined to be an elastic member which exerts a resisting force when its shape
is changed. Most springs are assumed linear and obey the Hooke's Law,
where F is the resisting force, Δ
is the displacement, and the k is the spring constant.
Basic
Spring Types
Springs are of several types, the
most plentiful of which are shown as follows,
We can expand the spring constant k
as a function of the material properties of the spring. Doing so and solving
for the spring displacement gives,
where G is the material shear
modulus, na is the number of active coils, and D and d are defined
in the drawing. The number of active coils is equal to the total number of
coils nt minus the number of end coils n* that do not help carry the
load,
The value for n* depends on the ends
of the spring. See the following illustration for different n* values:
 |
| Figure : An illustration of compression spring with different n* values [1] |
Shear Stress in
the Spring
The maximum shear
stress τmax in a helical spring occurs on
the inner face of the spring coils and is equal to,
where W is the
Wahl Correction Factor which accounts for shear stress resulting from spring
curvature,
To be continued
References :
- http://www.efunda.com/DesignStandards/springs/spring_design.cfm








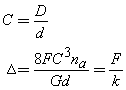


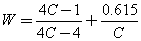
No comments:
Post a Comment